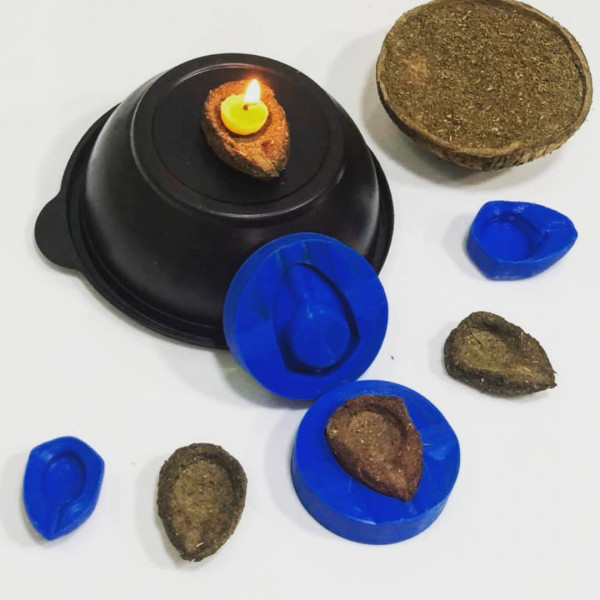
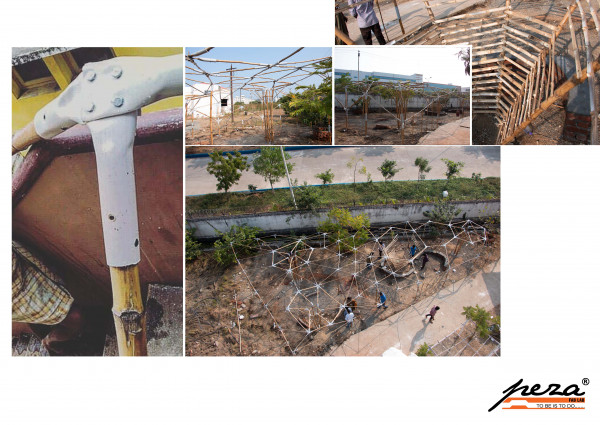
Design thinking is an approach used for practical and creative problem-solving. It is based heavily on the methods and processes that designers use (hence the name), but it has actually evolved from a range of different fields — including architecture, engineering and business. Design thinking can also be applied to any field; it doesn’t necessarily have to be design-specific.
What’s the difference between Solution-Based and Problem-Based Thinking?
As the name suggests, solution-based thinking focuses on finding solutions; coming up with something constructive to effectively tackle a certain problem. This is the opposite of problem-based thinking, which tends to fixate on obstacles and limitations.
What is the Design Thinking process?
As already mentioned, the Design Thinking process is progressive and highly user-centric. Before looking at the process in more detail, let’s consider the four principles of Design Thinking as laid out by Christoph Meinel and Harry Leifer of the Hasso-Plattner-Institute of Design at Stanford University, California.

The Four Principles of Design Thinking
- The human rule: No matter what the context, all design activity is social in nature, and any social innovation will bring us back to the “human-centric point of view”.
- The ambiguity rule: Ambiguity is inevitable, and it cannot be removed or oversimplified. Experimenting at the limits of your knowledge and ability is crucial in being able to see things differently.
- The redesign rule: All design is redesign. While technology and social circumstances may change and evolve, basic human needs remain unchanged. We essentially only redesign the means of fulfilling these needs or reaching desired outcomes.
- The tangibility rule: Making ideas tangible in the form of prototypes enables designers to communicate them more effectively.
The Five Phases of Design Thinking
Based on these four principles, the Design Thinking process can be broken down into five steps or phases, as per the aforementioned Hasso-Plattner-Institute of Design at Stanford (otherwise known as d.school): Empathise, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test. Let’s explore each of these in more detail.

Phase 1: Empathise
Empathy provides the critical starting point for Design Thinking. The first stage of the process is spent getting to know the user and understanding their wants, needs and objectives. This means observing and engaging with people in order to understand them on a psychological and emotional level. During this phase, the designer seeks to set aside their assumptions and gather real insights about the user. Learn all about key empathy-building methods here.
Phase 2: Define
The second stage in the Design Thinking process is dedicated to defining the problem. You’ll gather all of your findings from the empathise phase and start to make sense of them: what difficulties and barriers are your users coming up against? What patterns do you observe? What is the big user problem that your team needs to solve? By the end of the define phase, you will have a clear problem statement. The key here is to frame the problem in a user-centered way; rather than saying “We need to…”, frame it in terms of your user: “Retirees in the Bay area need…”
Once you’ve formulated the problem into words, you can start to come up with solutions and ideas — which brings us onto stage three.
Phase 3: Ideate
With a solid understanding of your users and a clear problem statement in mind, it’s time to start working on potential solutions. The third phase in the Design Thinking process is where the creativity happens, and it’s crucial to point out that the ideation stage is a judgement-free zone! Designers will hold ideation sessions in order to come up with as many new angles and ideas as possible. There are many different types of ideation technique that designers might use, from brainstorming and mindmapping to bodystorming (roleplay scenarios) and provocation — an extreme lateral-thinking technique that gets the designer to challenge established beliefs and explore new options and alternatives. Towards the end of the ideation phase, you’ll narrow it down to a few ideas with which to move forward.
Phase 4: Prototype
The fourth step in the Design Thinking process is all about experimentation and turning ideas into tangible products. A prototype is basically a scaled-down version of the product which incorporates the potential solutions identified in the previous stages. This step is key in putting each solution to the test and highlighting any constraints and flaws. Throughout the prototype stage, the proposed solutions may be accepted, improved, redesigned or rejected depending on how they fare in prototype form.
Phase 5: Test
After prototyping comes user testing, but it’s important to note that this is rarely the end of the Design Thinking process. In reality, the results of the testing phase will often lead you back to a previous step, providing the insights you need to redefine the original problem statement or to come up with new ideas you hadn’t thought of before.